Solution
Upon investigating the provided artifacts, we discovered that the ithelper account was newly created, and its PowerShell history revealed malicious activities including downloading network scanning tools and clearing event logs.
To determine when this account was created, we performed registry forensics on the SAM file.
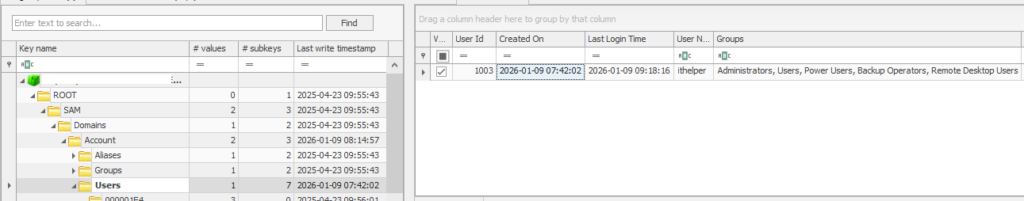
The ithelper account was created at 09-01-2026 07:42:02.
=> [1/5]: 07:42:02
Timeline analysis using $MFT and $J around this time revealed numerous files with the pattern C:\Windows\__<timestamp> being created.
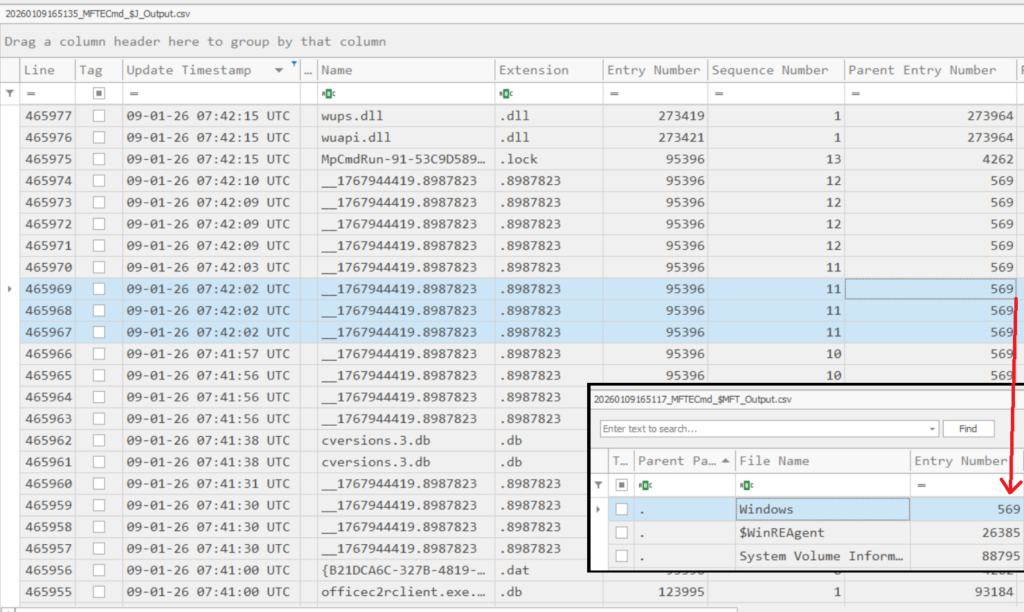
These files are not random. According to this article https://www.synacktiv.com/publications/traces-of-windows-remote-command-execution, the creation of these files indicates the use of wmiexec.py for remote command execution. When commands are executed via wmiexec.py, the output is written to these temporary files to redirect command output back to the attacker, after which they are immediately deleted. Each file creation corresponds to a single command execution, which explains the continuous creation and deletion pattern.
=> [2/5]: wmiexec.py
Searching the C:\Windows\__ directory or $MFT analysis revealed the existence of one such file that had not been deleted, likely because the command was interrupted during execution.
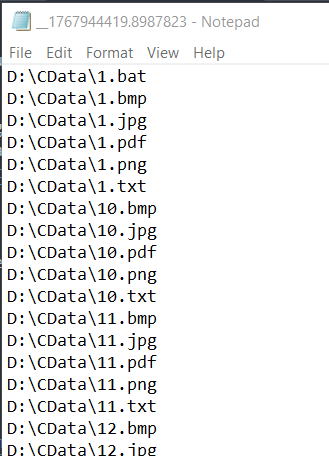
Based on the content, this file contains the output from listing files in the D:\CData directory.
=> [3/5]: D:\CData
Continued MFT timeline analysis showed the creation of the C:\Users\ithelper folder. This account was created by the attacker, and the creation of a user profile folder indicates that the account was logged into the machine. This evidence suggests the attacker used this account for RDP access, and the folder creation time corresponds to the first RDP login.
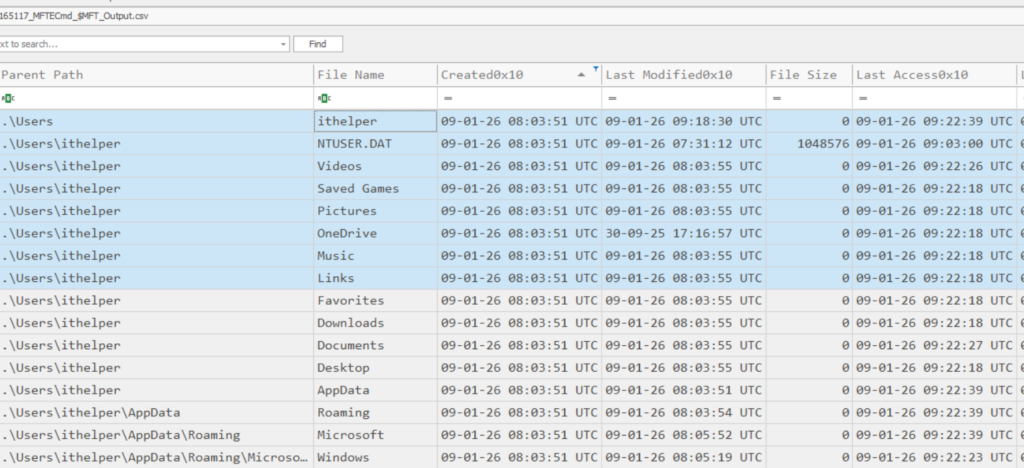
=> [4/5]: 08:03
Analysis of the ithelper PowerShell command history located at C:\Users\ithelper\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt revealed the command & "C:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" a -tzip out.zip "D:\CData\*", which was clearly executed to compress data for exfiltration. However, ConsoleHost_history.txt does not record timestamps for executed commands.
To recover timestamps for PowerShell commands stored in PSReadLine’s ConsoleHost_History.txt, correlate each append to the history file with the matching USN Journal DATA_EXTEND/DATA_ADDED record. The latest USN event aligns with the most recent command, and earlier commands follow in order from there.
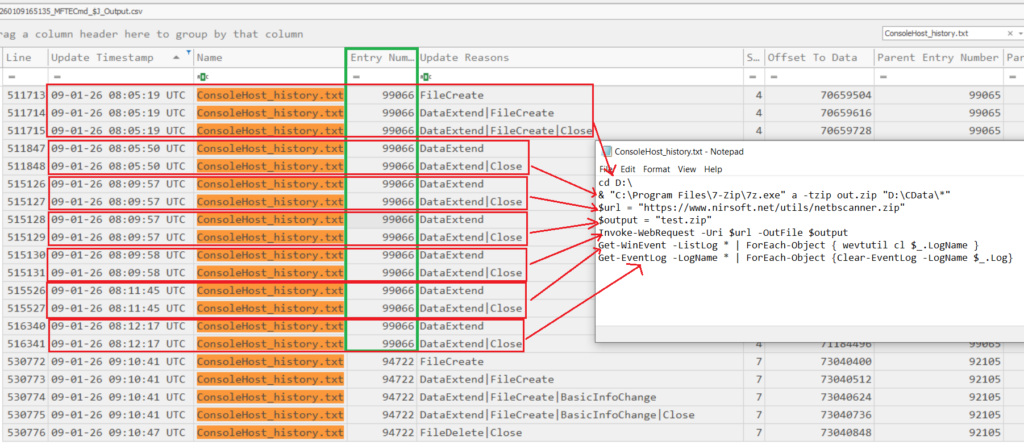
=> [5/5]: 08:05:50
Reference: [1]: https://www.synacktiv.com/publications/traces-of-windows-remote-command-execution
Note: The solutions presented here are not the only methods to solve each question.